Dr. Xiuqi Huang is from Visionox, which is developing OLEDs in China. He looked back to the time of the CRT – it was huge, heavy, but colourful. The TFT LCD then came along and was light and portable. OLEDs, on the other hand are a good candidate for flexible displays.
Dr. Xiuqi Huang is from Visionox, which is developing OLEDs in China. He looked back to the time of the CRT – it was huge, heavy, but colourful. The TFT LCD then came along and was light and portable. OLEDs, on the other hand are a good candidate for flexible displays.
Looking at flexible displays – the first stage is just to change the substrate to flexible, but a problem is that the cover glass is not so flexible and that has to be solved. The next step in flexible development is the creation of foldable OLED followed by rollable and freely flexible (even stretchable?).
Foldable products are available in a number of different types – infolding, outfolidng (depending if the front display is on the inside or outside) or both – and the features are different and pose different challenges. The outfolding type seems to be the best from the point of maturity of the technology, Huang said. There are lots challenges in foldable technology – oled encapsulation and laser delamination of the flexible OLED from the glass carrier on which the OLED is made is tricky. Flexible ic bonding is difficult and you need to control the stress on the display in the manufacturing processes.
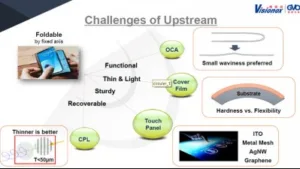
From the upstream side, the challenges are really flat material, the hardness/strength of the cover glass vs the flexibility, touch operation and thickness.
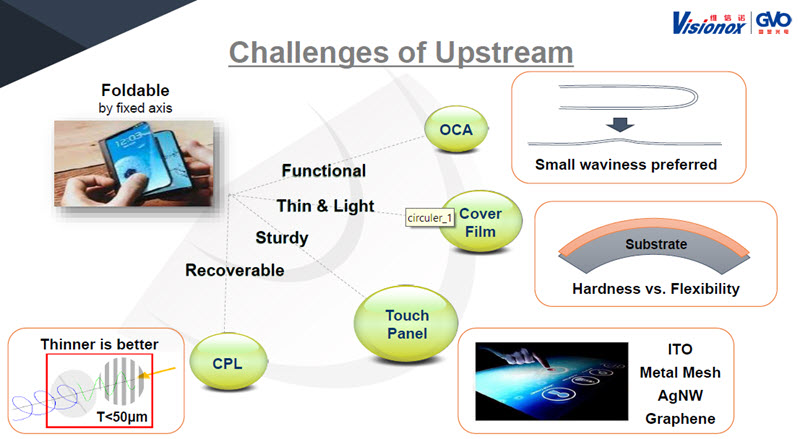 Dr Huang of Visionox detailed the upstream challenges of flexible OLEDs.
Dr Huang of Visionox detailed the upstream challenges of flexible OLEDs.
From the downstream side, the shape needs to be fashionable and attractive. Hinge design is very hard, he said and the display needs to be both reliable and durable.
To make flexible OLEDs, first you must have experience of rigid AMOLED and Visionox has been developing that with R&D experience in flexible.
The development needs industry and supply chain cooperation including the design of components and end products. If you have all these, then maybe a flexible OLED business is possible.
21 Years in the Business
Visionox has been in the OLED business for 21 years, moving from basic area OLEDs to PM OLEDs as displays and then to AMOLED. Huang said that Visionox is the only company making both PMOLED and AMOLED currently in China. It has one G5.5 line for AMOLED manufacture.
The company is making rigid AMOLEDs for wearables and for mobile phones and is trying to enter the vehicle display market. The company has made an OLED on a 0.2mm glass substrate and with thin film encapsulation, so that it is ultra-thin and the firm has a 5″ FHD OLED with a 0.6mm bezel.
The company has made PMOLEDs on flexible displays since 2001. The company started to develop the process in 2011 and in 2014 it made its first monochrome flexible display, then, again in 2014, it made its first colour one. In 2015, it made a very rollable display sample with full colour. In 2016, the firm made a 7″ foldable OLED with a radius of less than 3mm and tested it 40K times for folding.
The company has more than 2500 patents filed with 1000 granted and 200 patents on flexible displays.
Visionox has invested more than $1 billion in a G5.5 fab – its new line is a G6 costing $4 billion near Beijing in Gu’an (Yungu). On the G6, it will be trying to make rollable and foldable displays.
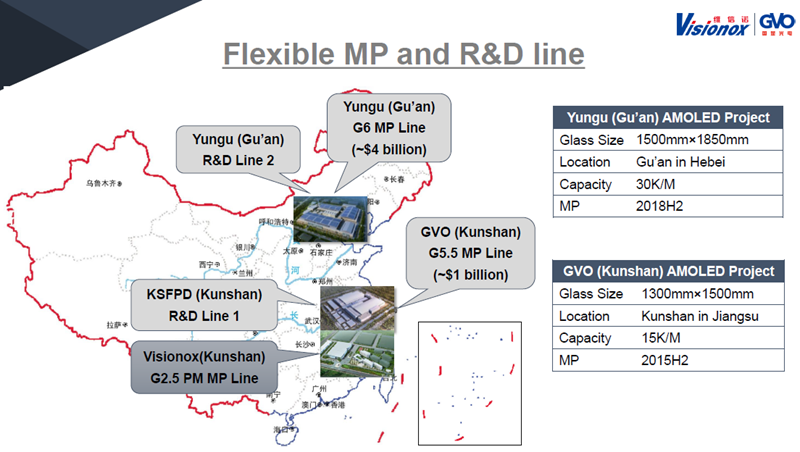 Visionox has invested a lot in OLED factories
Visionox has invested a lot in OLED factories
In conclusion, Dr. Huang said, there will be an evolution first small bezel displays, then foldable, then rollable and larger sized foldable.