Shoei Chemical of Japan has acquired Nanosys the leading quantum dots material supplier on September 6th, 2023. Quantum dots (QD) are key enabling technology for next-generation displays including MiniLEDs, QD-OLEDs and electroluminescent NanoLEDs providing growth opportunity for Shoei Chemical. Nanosys has been the first company to focus on quantum dots with >1000 unique product design-ins, >800 patents and applications and >140K kilograms of QD shipments. As of 2023, consumer electronics brands have shipped >70 million devices including tablets, monitors and TV based on Nanosys’ s proprietary quantum dot technology. Nanosys has been working with Shoei since 2019 and announced a partnership with the company in 2020 to expand QD manufacturing. Shoei will continue to operate the Nanosys brand and Silicon Valley-based R&D facility. Major benefits will be coming in future in terms of expanded capabilities and resources. What will be the implications for the QD display industry?
QDEF Plus MiniLED: Potential for Higher Growth with More Efficient Supply Chain
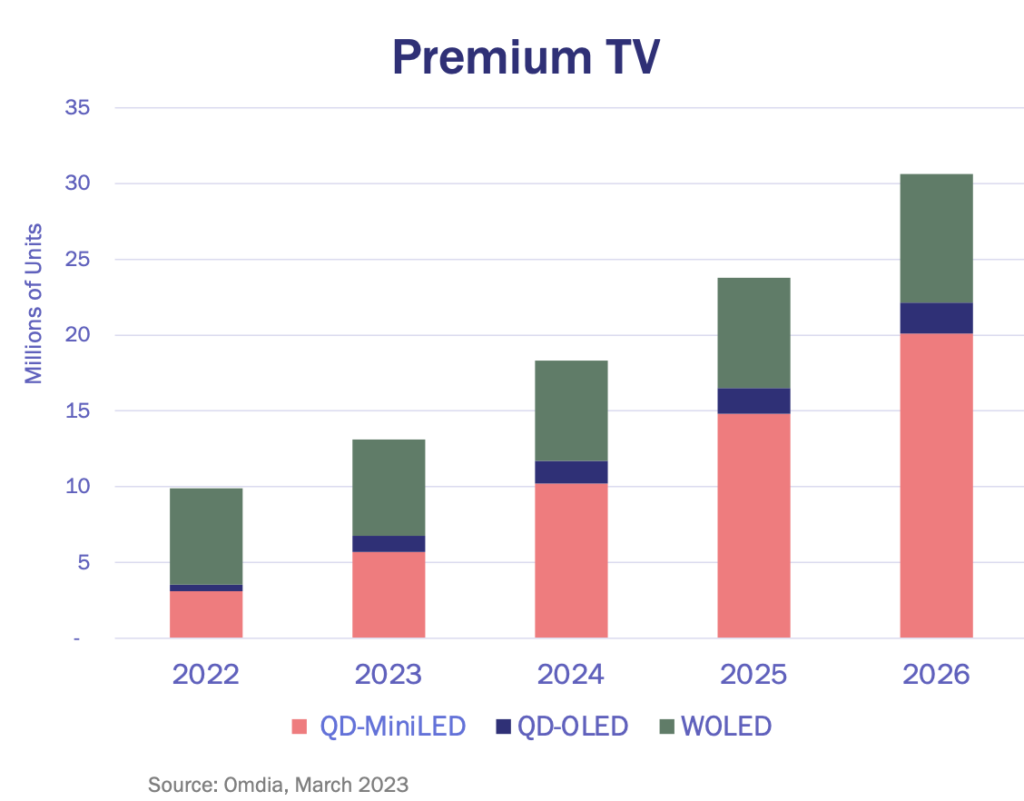
QD enhancement film (QDEF) enabled LCD TV to have a wider color gamut (WCG), better color purity, very high brightness, and more immersive HDR experience while maintaining power efficiency. The cost of QDEF film has reduced considerably in recent years enabling a combination of MiniLED and QD backlight LCD TV for the premium market. By the use of multi zone dimmable backlights, MiniLED with QDEF has enabled LCD to display performance close to OLED. There have been 100% attach rates for QD in MiniLED TV. QD technology is also evolving with new processors, new materials, and new product offerings. Nanosys has introduced xQDEF diffuser plate with precise light diffusion necessary for higher contrast levels in MiniLED and full-array-local-dimming (FALD) LCDs. The xQDEF diffuser plate can simplify the display assembly process, enabling lower costs. Most of the top TV manufacturers such as Samsung, LG, Sony, TCL, Hisense, Vizio, and Skyworth have already adopted QD display technology in their TVs. It has enabled LCD technology to reinvent itself and has created growth opportunities in the TV market especially when combined with MiniLED backlights.
MiniLED QD TV is the best-performing LCD TV in the market but it still lags OLED TV in terms of shipments and revenue. It has the potential to offer even stronger growth in future years by offering larger, higher performance, thinner and more power efficient TV at a lower cost. Cost is still a big challenge. With significant cost improvement, it could trigger a faster replacement cycle for TV, enabling MiniLED QD TV to outperform OLED TV shipments in the future. A paper by BOE’s S.W. Yang at Display Week 2023 symposium proposed, “A small aspect ratio high voltage Mini LED solution that can realize low-cost glass-based MLED backlights”. According to his conclusion, “In general, this solution can greatly improve the cost- effectiveness of MLED backlight products, enabling COG MLED to have technical advantages while overcoming the disadvantage of higher cost than PCB. It plays an important role in promoting COG Mini LED backlight products to seize the first opportunity in the MLED industry, and can be widely used in a full range of Mini LED backlight products such as commercial display, TV, MNT, NB, automotive, and VR”.
According to Jeff Yurek, VP of Marketing for Nanosys, “We’re excited about what this acquisition means for the near-term growth of Quantum Dots. Shoei’s proven ability to produce Quantum Dots at scale, their proximity to our key customers – over 95% of whom are outside the U.S.– and their ability to accelerate the development of our next-generation technologies made them a natural fit to acquire Nanosys. As of this year, Shoei is already producing 100% of Nanosys quantum dot materials. So this should be a seamless transition for our customers.” Shoei can provide scale and efficiency needed for lower cost and higher supply of QD materials. With technology developments and more efficient supply chain for QD material, MiniLED QD TV will have higher growth opportunity.
QD-OLED: Better Development for Next Generation Products
QD color conversion technology has been used by Samsung Display to introduce QD-OLED display at 2022 CES. The company now has 65”, 55” and 77” QD-OLED TVs and 34” and 49” monitor panels. Sony and Samsung Electronics are offering QD-OLED TV and Samsung Electronics and Dell Alienware are offering QD-OLED gaming monitors. QD-OLED technology of blue OLED display with printed quantum dot layer color conversion and sub-pixel level dimming, display can achieve expanded color gamut, higher color volume, and color luminosity. However, blue emitting materials still have efficiency and lifetime issues. UDC has announced that they expect to meet preliminary target specs with their phosphorescent blue. The use of phosphorescent blue can help to reduce multiple layers, increase efficiency and lifetime. It can also help to reduce costs and expand existing capacity by reducing the number of blue layers. QD-OLED products sales are increasing.
According to Chirag Shah’s presentation at Business conference of DW23, in 2023, QD-OLED with hyper efficient EL material, advanced optimization algorithm InteliSense AI, and advanced Cd Free quantum conversion material has been able to achieve 33% more color and brightness reaching >2000 nits. Samsung Display has developed a new metric called XCR (Experienced Color Range) which measures “The Real Feel of Color” showing increase in color saturation causes perceived increase in brightness.
Perceived brightness(Q) = Achromatic Luminance (white) + Chromatic Luminance (color vividness).
Nanosys’s paper by Jen-La Plante and others at DisplayWeek 2023 pointed out that, “As the technology of QDCC further matures, the size of the blue driving backlight pixel will continue to decrease in size due to two primary driving factors. First, as QDCC expands to small format displays like watches and mobile devices, the blue backlight pixel will shrink in size as a response to increasing demands for screen resolution. Second, for larger format displays like television and monitors, the high costs of epitaxial thin film growth on a per area basis may drive adoption of smaller backlights”. QD material developments enable these next gen products. OLED technology is expected to go through major improvements in next few years with development of all phosphorescent RGB, improvement in material performance and higher production with multiple suppliers bringing in Gen 8.7 OLED fab capacity. Competition will be fierce with QD-LCD and OLED. As per Jeff Yurek, “Shoei stands for dependability and trust. Nanosys is all about innovation. Shoei plus Nanosys brings together dependability with innovation in what I think is a powerful combination. Together we’ll be able to push quantum dots further and deliver those innovations at scale.”
QD-MicroLED: Higher Potential for Manufacturing Improvements
The mass transfer process that requires bonding RGB (Red Green Blue) MicroLED to the display backplane accurately and efficiently is very challenging. Color conversion by Quantum Dots (QDs) (QDCC) or by phosphor provides another alternative. Using single-color (blue) MicroLED chips and color converting them with QD layers can help in the manufacturing process. Many companies have shown prototypes and developing this technology further. AUO has also developed its rollable MicroLED display using a color conversion layer to form the red sub-pixels. Through the color conversion material, the blue light is converted into red light. As per AUO’s paper by C.J. Liu at DisplayWeek 2023, “Blue MicroLEDs have better thermal stability than red MicroLEDs. Therefore, the reliability of displays will be improved even at high ambience temperature. The efficiency of red sub-pixels was also increased by using the color conversion technique with blue MicroLEDs”.
Nanosys’s presentation at DisplayWeek Business Conference this year showed, “QDCC on UV MicroLED enables high brightness, superior color quality, and high resolution with cost-effective manufacturing”. Applied Materials has introduced a novel and scalable approach to fabricate MicroLED displays using high efficiency UV MicroLEDs with 4-subpixel layout, and in-situ curing Cd-free R/G/B quantum dot formulation. The company has developed a prototype of a 1.37” smart watch display UV-A MicroLED with LTPS backplane. Applied Material’s UV-A MicroLEDs and Cd-free RGB QDs with high-EQE, high-efficiency, simplified mass transfer and pixel repair scheme by 4th subpixel can improve manufacturing yield and reduce production cost. Nanosys and Shoei together can enable even higher manufacturing improvements for QD-MicroLED.
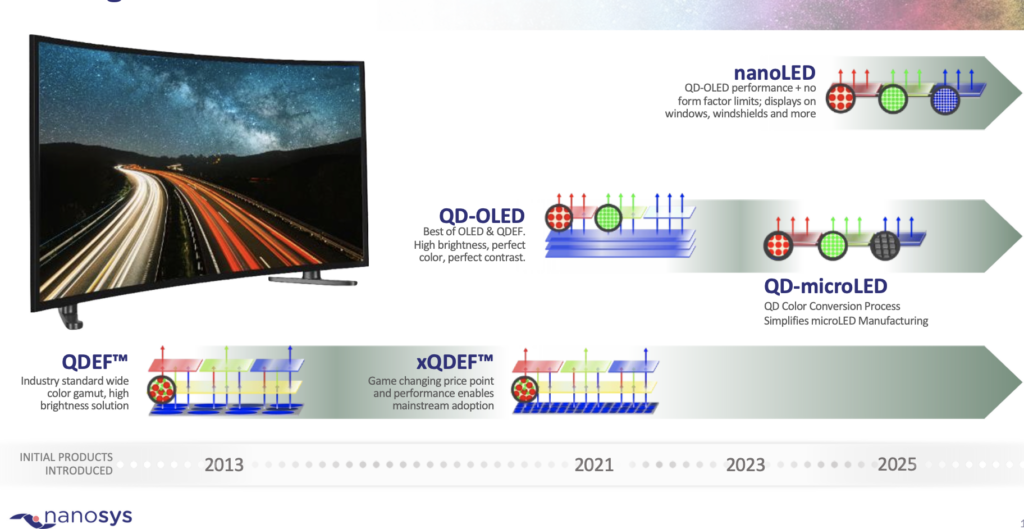
QD NanoLED: Opportunity for Lower Cost Emissive Product
NanoLED, an emissive display, has the advantages of perfect black, better color, and wider viewing angle. It also provides true HDR luminance and higher reliability (inorganic materials). However, the biggest attraction for this next generation display is the potential for ultra-thin flexible displays at low cost with its solution process printed manufacturing. NanoLED display sometimes referred as QD-LED or QD-EL which is based on QD’s electroluminescence to directly produce 3 (RGB) primary colors in to each pixel. BOE has developed a 55-inch 8K active matrix QLED (QD-EL) using inkjet printing. Inkjet process still has issues and still requires more research. According to BOE’s paper by Y. Zhang at DisplayWeek 2023, “The successful fabrication of 8K display verifies the possibility of mass production of AMQLED large-size high-resolution display technology, and provides a technical basis for the development of quantum dot display technology in the future”.
Samsung has demonstrated all ink-jet-printed 12.4” full color EL-QD panel with cd-free RGB QDs in the top emission structure by inkjet printing of all layers except electrodes. According to Samsung paper by J. Ha at DisplayWeek 2023, “Inkjet-printing of self-emissive displays based on organic light- emitting materials (OLEDs) or QDs (EL-QD) is a promising technology for saving manufacturing costs by drastic improvement of material consumption efficiency compared to the current thermal evaporation method of OLED panels. The use of expensive fine metal masks is negated in inkjet-printing. Further reduction in the initial capital investments can be made for all-inkjet-printing (AIP) process by eliminating relevant manufacturing process steps, reducing the total manufacturing cost by ~25% in comparison to white OLED. Especially, inkjet-printing is most suitable for producing EL-QD displays by formulating inks with RGB QDs and charge transport layers”. The solution-processing method, however, is complicated with difficulties in the formation of a well-defined multi-layer structure.
Sharp has successfully developed an active matrix NanoLED display using RGB cadmium free QDs patterned by their photolithography process in the atmosphere. According to Sharp’s paper by S.Okamoto at DW2023, “Photolithography is a widely used technology in the manufacture of electronic devices and flat panel displays industry such as in the fabrication of backplanes. It can also be an effective technique for QDs patterning, considering that the manufacturing equipment is already installed in display factories”. The paper concluded, “We expect that NanoLED will evolve as a technology that will revolutionize the display industry, just as the previous generation of LCDs and OLEDs did”.
Jeff Yurek of Nanosys said, “Electroluminescent Quantum Dots, or NanoLED as we call it, is the future display technology. NanoLED can deliver incredible performance from inorganic quantum dot emitter materials in terms of brightness, color and contrast. More importantly, it can be disruptively low cost since NanoLED displays can be made using solution processing. We can get rid of the costly evaporative steps and large vacuum chambers that are used in display making today. It’s incredibly exciting and it’s not too far off it is closer to commercialization than I think many people realize. Shoei is committed to the future of quantum dot technology and we’re excited to accelerate progress in NanoLEDs as a part of Shoei.“
With matured display applications market and slower market demand, technology innovations and cost reductions can help to drive replacement demand. If acquisition of Nanosys by Shoei can deliver technology innovation with lower costs, it will be good for the Quantum Dot display market.

Sweta Dash is the founding president of Dash-Insights, a market research and consulting company specializing in the display industry. For more information, contact [email protected] or visit www.dash-insights.com

