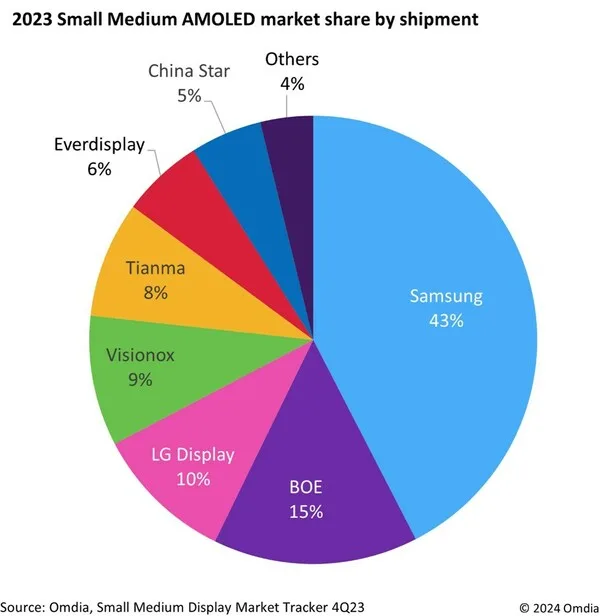
The Korean press is in a tizzy as surging competition from Chinese display manufacturers is forcing Samsung Display to significantly increase its workforce dedicated to developing smaller OLED panels. This adjustment comes in light of the company’s diminishing share in the global AMOLED market, dropping to 43% in 2023 from a previous 56%, while Chinese rival BOE saw an uptick in its market share from 12% to 15%, according to data from Omdia. It may not quite be a panic yet, but that could all change as Chinese manufacturers get closer to South Korea’s display giants on OLED.
Samsung Display has reallocated approximately 500 engineers, about 30% of its large OLED panel workforce, to focus on small and medium-sized OLED displays amidst the onslaught from Chinese companies. The smaller OLED panel sector is witnessing a significant surge in demand, driven by the rising interest in new product categories such as automotive displays, contrasting with stagnant demand in the large panel segment. Projections by Omdia suggest the market for smaller OLED panels is set to expand dramatically, expected to more than triple to $8.9 billion by 2029 from $2.5 billion projected for this year.
Samsung Display’s strategic shift underscores how South Korean firms are being forced to restructure to maintain dominance in the OLED sector amidst formidable competition from Chinese manufacturers. Samsung Display is also investing heavily in protecting its technology lead, including the construction of the world’s first 8.6-generation IT OLED line in South Korea, aimed at commencing mass production in 2026. This new manufacturing line is expected to counter better pricing from Chinese competitors and double production capacity relative to existing facilities. Similarly, LG Display has announced substantial investments aimed at bolstering its production capabilities in smaller OLED panels. But Chinese firms like BOE are not getting left behind and are also committing significant resources to expand their presence.

