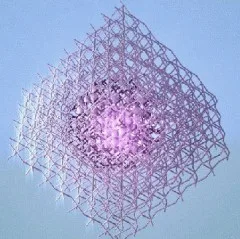
 Image credit:Sargent Group/University of Toronto, EngineeringScientists at the University of Toronto have published results of tests on a new “hyper-efficient” light-emitting crystal formed by combining perovskite and colloidal quantum dots (QDs) using heteroepitaxy. A “scaffold” of QDs is created, then the perovskite crystal is grown around it. Growing them this way avoids faults at the seams between the materials and allows the high efficiency.
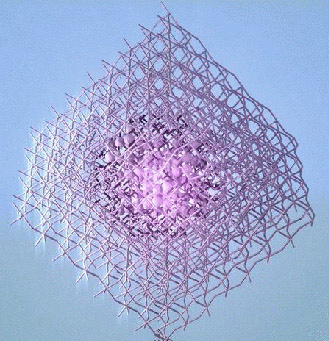
Image credit:Sargent Group/University of Toronto, EngineeringScientists at the University of Toronto have published results of tests on a new “hyper-efficient” light-emitting crystal formed by combining perovskite and colloidal quantum dots (QDs) using heteroepitaxy. A “scaffold” of QDs is created, then the perovskite crystal is grown around it. Growing them this way avoids faults at the seams between the materials and allows the high efficiency.
In an interview with Photonics.com, Dr. Riccardo Comin said that the group has found that the material solves the “re-absorption” problem that some materials re-absorb light of the same colour that has been emitted.
The group believes that it can design near-infrared LEDs that can beat the efficiency of current devices.
Separately, Imec announced at its Imec Technology Forum that it has achieved a “record” 11.9% active area conversion efficiency for its thin-film perovskite photovoltaic module.
Analyst Comment
As Matt reported back in December (Top LED and Laser Technologies for Displays from 2014), perovskite is not a single material, but a family of materials and is attracting a lot of interest among researchers around the world.
Interestingly, Philips lighting told us at the Display Summit that its new ColorSpark technology also solves the problem of re-absorption, but wouldn’t tell us how it is doing it or what the material is. (BR)