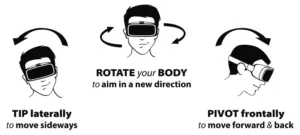
MonkeyMedia, an independent R&D lab with a 25-year track record of developing technology experiences, has announced the launch of its patented, body-based navigation solution, BodyNav, for hands-free virtual reality interactions. BodyNav leverages the existing on-board sensors of smartphones and 3D headsets to engage the body’s innate centre of gravity. This human-centred interaction approach is claimed to reduce motion sickness and enhance navigation abilities in VR and AR, as well as first-person-view drone aviation.
Motion sickness has long been a complaint amongst virtual reality gamers and drone pilots. BodyNav uses distinct sensor axes for independent functions to try to maintain equilibrium in the body’s proprioceptive system. Viewers simply lean, using either their head or torso, to move themselves through virtual spaces, or to move their drones through remote physical spaces. This allows the sensory receptors, which receive stimuli internally and relate to the body’s position and movement, to properly engage with virtual or remote content, synchronising visual and vestibular senses and reducing motion sickness-inducing factors.