Research teams from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Shanghai University have developed a strategy for efficient and stable deep-blue organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), an advance that could improve the quality of screens in smartphones, tablets, and large TV screens. OLEDs are energy-efficient as they do not require additional background illumination. They can also be created using low-cost thin-film technology and can work on flexible materials, allowing for bendable displays and adaptable room lighting solutions. While red and green OLEDs are commercially available and reliable, blue OLEDs have been problematic due to their inability to maintain high efficiency, high luminance, and a long lifespan. The research focused on overcoming the challenges in producing blue OLEDs as they tend to be fainter and fade faster than their red and green counterparts.
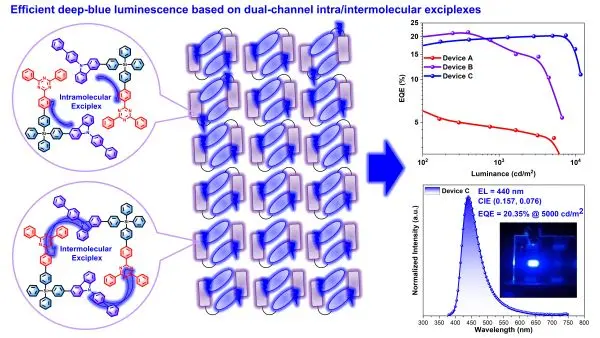
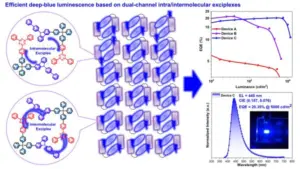
To address this, the researchers developed a new molecule (CzSiTrz) that linked carbazole and triazine fragments with a silicon atom. When these molecules assemble into nanoparticles, electronic excitation results in a dual-channel intra-/intermolecular exciplex emission, allowing the deep-blue OLEDs to shine more efficiently and stably. An exciplex is an electronically excited molecular complex with a unique emission differing from the emissions of excited individual molecules.
The newly developed deep-blue OLEDs demonstrated a record external quantum efficiency of 20.35 percent, reflecting the ratio between radiation output and power input. They also achieved a high luminance of 5000 candela per square meter (cd/m2). The synthesized molecule and the production components could open the way for a new generation of efficient and long-lasting deep-blue OLEDs.
Reference
Zhang, Z., Dou, D., Xia, R., Wu, P., Spuling, E., Wang, K., Cao, J., Wei, B., Li, X., Zhang, J., Bräse, S., & Wang, Z. (2023). Efficient deep-blue luminescence based on dual-channel intra/intermolecular exciplexes. In Science Advances (Vol. 9, Issue 20, p. eadf4060). https://www.science.org/doi/abs/10.1126/sciadv.adf4060