TCL CSOT’s ΔE color accuracy improvement technology is a major first for the company, and the world if you believe the announcement. After two years of development, TCL CSOT’s technical team successfully has created first of its kind color accuracy adjustment at the monitor or panel level. This is compared to making color adjustments through software algorithms on the system side.
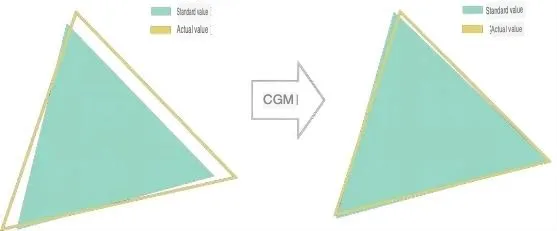
ΔE is a standard formulated by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) to measure the difference between a display’s color and the original color standard of the input content. The lower the ΔE value, the higher the color accuracy. The ΔE adjustment technology works by calibrating each screen segment to align its color point with the standard point of the required color. This process enhances the color fidelity of the display. he technology considers various color standards like sRGB, DCI-P3, and Adobe RGB, catering to different professional needs and industries.
The ΔE color accuracy improvement technology appears to be a sophisticated, technical endeavor integrating both hardware and software innovations. At the heart of this process is the application of the technology at the monitor module level, implying a direct integration within the monitor’s hardware components. This integration likely involves the precise calibration of LCD panels and the optimization of backlight LEDs to ensure uniformity and accuracy in color reproduction.
The core algorithm, CGM IP (color gamut management intellectual property), plays a crucial role in this process. It represents a fusion algorithm that likely combines elements of color science, digital signal processing, and perhaps machine learning algorithms to automatically and efficiently adjust color outputs. This algorithm addresses the key pain points of resource intensity and suboptimal performance in traditional color calibration methods. By applying this algorithm, TCL CSOT ensures that each screen segment is individually calibrated, aligning the color point of the screen with the standard point of the required color. This piece-by-piece calibration is essential for achieving a high degree of color fidelity across the entire display.
Additionally, the manufacturing process enhancements and design optimizations in panel and backlight components suggest this comprehensive approach to maintaining color accuracy is working throughout the build process for a monitor. The result of this intricate combination of hardware calibration and sophisticated software algorithms is a display that can accurately render colors as close to the original standards (like sRGB, DCI-P3, Adobe RGB) as possible, across different usage scenarios and professional requirements.
Color Calibration is Rote
Color calibration of monitors is a crucial process, especially in fields where accurate color reproduction is essential, such as graphic design, photography, and video editing. This procedure typically involves both hardware and software adjustments. Initially, a colorimeter or spectrophotometer, which are hardware devices, are selected for the calibration. The ambient lighting of the room is also taken into consideration for consistency and optimal brightness.
The calibration is largely driven by specialized software, which comes with these hardware devices. This software is essential for guiding the user through the calibration process. It displays a range of colors and shades on the monitor, which the calibration device then measures. Before beginning the calibration, some basic display settings, such as brightness, contrast, and color temperature, are manually adjusted according to the software’s recommendations.
During the calibration, the device placed on the screen reads the displayed colors and compares them to standard values. This results in the creation of a color profile specific to the monitor, adjusting the display to match standard color values as closely as possible. This color profile is then applied and saved, ensuring consistent and accurate color display. It’s important to note that while the hardware device measures color accuracy, the adjustments made are typically within the monitor’s software settings, rather than physical adjustments to the monitor’s hardware. Regular recalibration every few months is recommended to maintain color accuracy, as the colors a monitor displays can drift over time.

