Panasonic Corporation today announced that it has commercialized an encapsulation material having a high dielectric constant that is suitable for finger-print recognition sensor packages to be incorporated in mobile devices, and will start full-scale mass production of the product in April 2016. This material helps improve the performance as well as reduce the size and thickness of packages for finger-print recognition sensors.
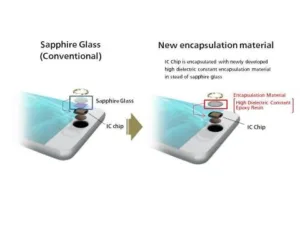
Finger-print recognition features are expected to be embedded in an increasing number of mobile devices including smartphones. Sapphire glass has been used in the finger-print contact part of packages for existing capacitive finger-print recognition sensors due to its high dielectric constant, but has drawbacks such as the difficulty of making the sensor packages smaller and thinner and the complexity of the manufacturing processes. Panasonic has commercialized an encapsulation material having a high dielectric constant that can be used instead of sapphire glass. This material will help improve the performance as well as reduce the size and thickness of sensor packages.
This encapsulation material has the following advantages.
- High relative permittivity: Meeting the demand for higher sensitivity of sensors and smaller, thinner packages
?Relative permittivity (at 1 MHz): up to 20 (approximately 10 with sapphire glass)
?Twice the sensitivity of sapphire glass - Narrow-part filling and low warpage during molding: greater flexibility in the design of packaging structures
?Narrow-part filling: supporting 50-?m encapsulation thickness on the chip (compression molding)
?Low warpage: available in a wide lineup in accordance with packaging structures - Ready for packaging thinner structures with simplified manufacturing processes