Broadcast & Distribution – Elemental Technologies delivered a webinar titled, “Creating scalable workflows for file-based video delivery.” It laid out several architectures that content delivery providers are able to configure – with Elemental products, of course.
According to presenter Mike Callahan, Senior Director of Product Marketing at Elemental, some of their customers are now moving to adopt more advanced solutions that scale up or down as needed and that can create new revenue streams via ad insertion. Just after the webinar, Elemental also announced it had complete a series D funding round worth $14.5M with strategic partners Telstra (a big Australian Telco) and Sky (an entertainment leader in Europe) (see release).
Elemental is a software company that has embraced the virtualization trend. While it does sell its own servers and hardware, they are based upon off the shelf CPU and GPU components and come pre-loaded with their software. These assets can sit at a customer’s site, in the cloud or at the network edge, depending on your needs. They call their solution Software Defined Video (SDV).
One of the obvious trends in content consumption is the move t0 mobile platforms for viewing. This is combined with a desire to see this content anytime and anywhere. A typical use case might be viewing live linear content on your TV to start – let’s say it is a sporting event. You then want to continue watching this content on your tablet in the kitchen. Maybe you have to leave the house to go get some beer, so you want to check the game in the liquor store. This requires a catch-up capability so you can play back content you may have missed – including that important score. Getting the content in the store may requires you to have access via the cellular networks or wifi hotspots and it may have to validate that you have a TV subscription with a content provider.
On the other hand, you just may too busy to watch the game live, so maybe you want to record it or play it back later using a VOD service. Will that VOD playback show the same ads from the original broadcast, or can the delivery provider insert alternative ads to create a new revenue stream?
These are the real scenarios and business questions that face the industry today – and the ones that Elemental is trying to address.
In the webcast, Callahan described several architectures. The first is what he termed “simple” – and the one that most delivery providers are using now. At the center is the Elemental Server which is a big transcoding appliance. It ingests content in multiple audio and video encoded formats and transcodes the content to a consistent set of formats that the provider needs. This includes advertisements too. The server then encapsulates the content in the desired streaming formats such as MPEG-DASH, Apple HLS, MS Live Smooth Streaming, etc. A second platform called Elemental Delta, sits at the network edge, typically. It is responsible for managing the VOD service to end users, directing the formatted content to validated viewers. 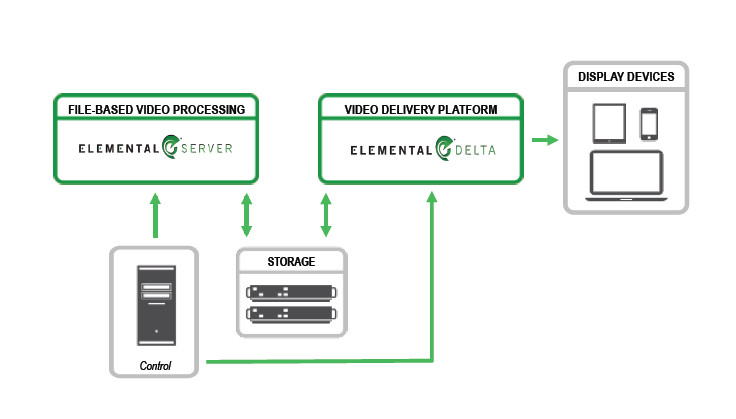 Elemental Basic Config Callahan then described two intermediate solutions that build on the simple one. The first is the ability for the content delivery partner to interface with the Elemental server using a third party content management solution like Aspera. There are several of these types of solutions deployed that can add metadata to the content, so Elemental allows easy interfacing with then to control the ingest and transcode process.
Elemental Basic Config Callahan then described two intermediate solutions that build on the simple one. The first is the ability for the content delivery partner to interface with the Elemental server using a third party content management solution like Aspera. There are several of these types of solutions deployed that can add metadata to the content, so Elemental allows easy interfacing with then to control the ingest and transcode process. 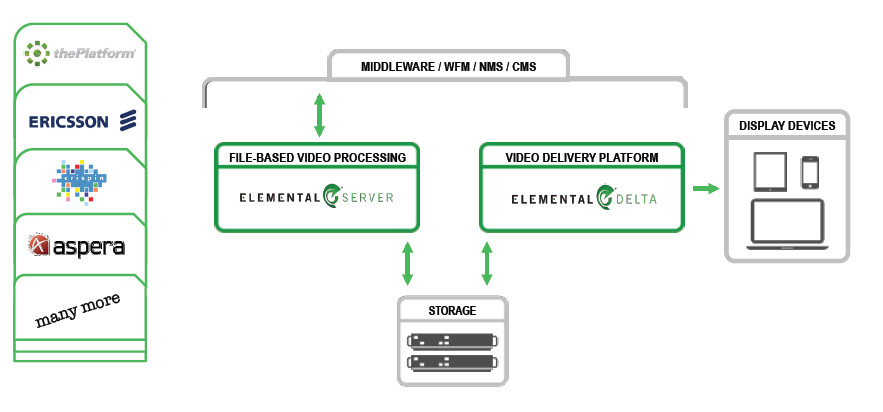 For clients where the volume starts to get large, Elemental can scale their solution. That means adding more Elemental Servers and Elemental Delta platforms. But when you do this, you need to add the third component: Elemental Composer. This is a management tool that helps to properly allocate the resources for the job at hand. It also manages any upgrades so these are done once, then pushed to the other platforms in the configuration. The advanced solution takes this architecture to the cloud so that the content provider does not have to buy or maintain these assets – they pay for the services as needed. This has great scalability too allowing an increase and decrease in assets as needed.
For clients where the volume starts to get large, Elemental can scale their solution. That means adding more Elemental Servers and Elemental Delta platforms. But when you do this, you need to add the third component: Elemental Composer. This is a management tool that helps to properly allocate the resources for the job at hand. It also manages any upgrades so these are done once, then pushed to the other platforms in the configuration. The advanced solution takes this architecture to the cloud so that the content provider does not have to buy or maintain these assets – they pay for the services as needed. This has great scalability too allowing an increase and decrease in assets as needed. 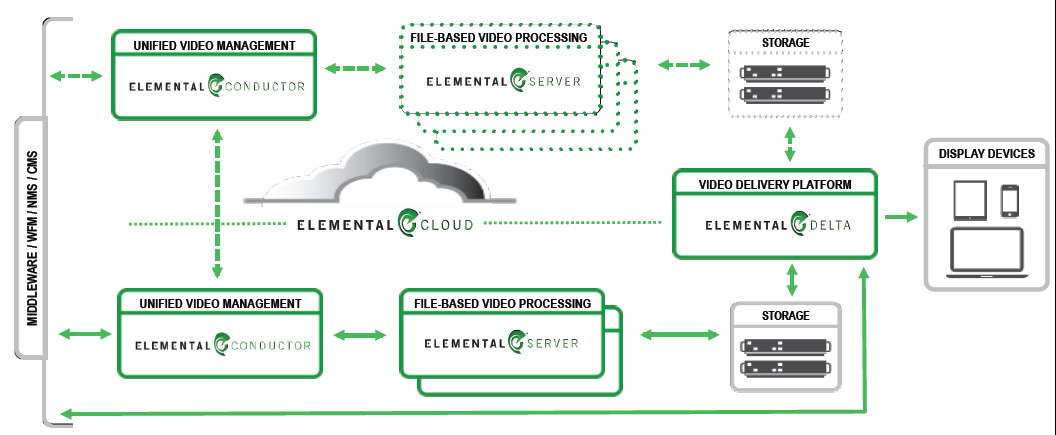 The extreme solution has all this plus redundancy. One of the applications that Callahan pointed to was the CNNgo app, which we profiled previously. CNNgo is a blending of live feed and on-demand video – a kind of fusion broadcast model that may be more widely adopted. CNN curates this content offering a series of related videos to allow users to easily gather more details or data. The content is only CNN content, however. And, it allows for the insertion of new advertisements into the content, creating more revenue for CNN. These capabilities are all built into the Elemental Delta product. This is represented in the architecture below.
The extreme solution has all this plus redundancy. One of the applications that Callahan pointed to was the CNNgo app, which we profiled previously. CNNgo is a blending of live feed and on-demand video – a kind of fusion broadcast model that may be more widely adopted. CNN curates this content offering a series of related videos to allow users to easily gather more details or data. The content is only CNN content, however. And, it allows for the insertion of new advertisements into the content, creating more revenue for CNN. These capabilities are all built into the Elemental Delta product. This is represented in the architecture below.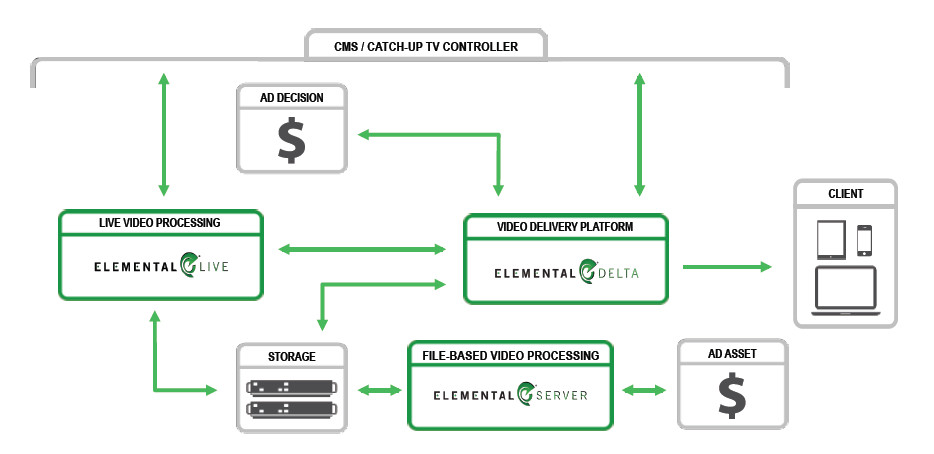 Elemental live VOD with frame accuracy Elemental live VOD with frame accuracy[/caption] Elemental’s infrastructure is fully ready to support 4K-UHD workflows including encoding with HEVC. DRMs are also available for content protection. In the Q&A part of the webinar, Callahan noted that the firm now has about 500 customers from small TV stations to top TV providers. Many have simple workflows now, but a few are moving to advanced workflows with ad insertion, which he expects to become more popular soon. –Chris Chinnock
Elemental live VOD with frame accuracy Elemental live VOD with frame accuracy[/caption] Elemental’s infrastructure is fully ready to support 4K-UHD workflows including encoding with HEVC. DRMs are also available for content protection. In the Q&A part of the webinar, Callahan noted that the firm now has about 500 customers from small TV stations to top TV providers. Many have simple workflows now, but a few are moving to advanced workflows with ad insertion, which he expects to become more popular soon. –Chris Chinnock

