Ingress Protection (IP) ratings are defined by the international standard IEC 60529, which classifies the degrees of protection provided against the intrusion of solid objects (including body parts like hands and fingers), dust, accidental contact, and water in electrical enclosures. The IP rating consists of two digits, where each digit represents a specific type of protection.
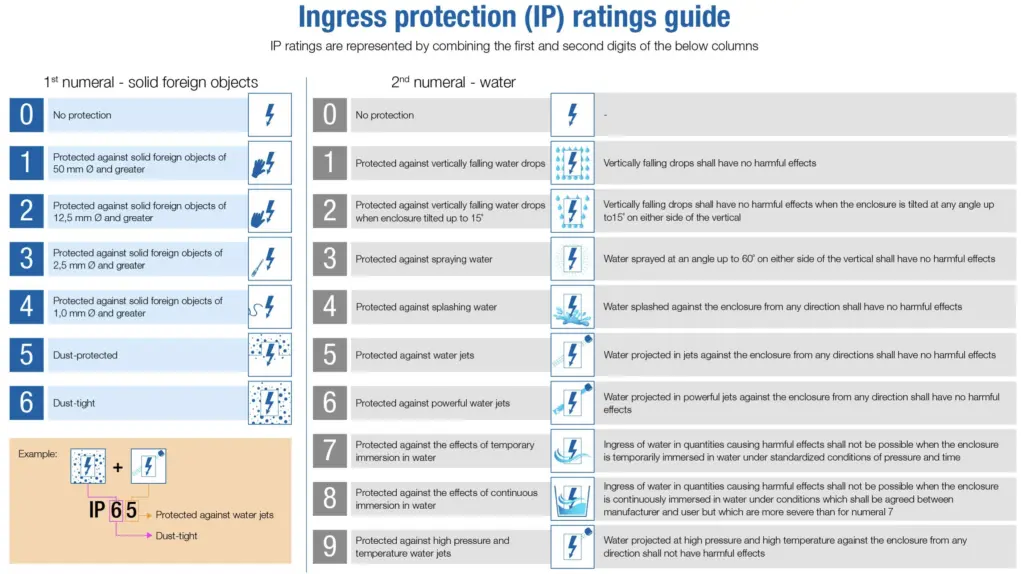
The first digit, ranging from 0 (no protection) to 6 (dust-tight), indicates the level of protection against solid particles. In the case of IP68, the ‘6’ means that the device is completely protected against dust ingress. It prevents any dust particles from entering the device’s enclosure, ensuring that its internal components remain free from dust contamination. This is particularly important for electronic devices, as dust buildup can lead to overheating, reduced performance, and potentially damage the components.
The second digit, ranging from 0 (no protection) to 8 (protection against continuous submersion), represents the device’s level of protection against water ingress. The ‘8’ in IP68 signifies that the device can be submerged in water up to a certain depth, typically around 1.5 meters (4.9 feet), for a specific duration, usually up to 30 minutes, without any harmful effects. This is achieved through the use of gaskets, seals, and other waterproofing techniques to prevent water from entering the device’s enclosure and damaging its internal components.
It is essential to note that IP68 ratings are manufacturer-specific and may vary in terms of actual depth and duration of water submersion. Users should consult the device’s documentation for precise information on its water resistance capabilities.
About IEC
IEC stands for the International Electrotechnical Commission. It is an international standards organization responsible for preparing and publishing consensus-based standards, technical specifications, and guidelines for electrical, electronic, and related technologies. Founded in 1906 and headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, the IEC promotes international cooperation on all aspects of electrotechnical standardization and related matters.
The IEC brings together experts from around the world to develop and maintain standards that ensure the safety, efficiency, reliability, and interoperability of electrical and electronic devices, systems, and technologies. These standards facilitate international trade by providing a common set of technical specifications that manufacturers and industries can follow, ensuring that their products are compatible and can be used safely across different markets.
IEC standards cover a wide range of fields, including power generation, transmission, and distribution, renewable energy, electronics, semiconductors, electromedical devices, and information technology. One of the well-known standards developed by the IEC is the Ingress Protection (IP) rating system (IEC 60529), which classifies the degrees of protection provided by electrical enclosures against the intrusion of solid objects and liquids.

