As the demand for super-large TV displays grow, the need for higher resolution is set to increase, and 2018 will see the first uses of 8K display, according to IHS Markit.
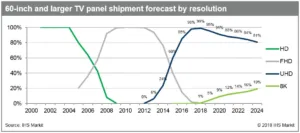
While Ultra HD panels are estimated to account for more than 98% of the 60″-and-larger display market in 2017, most TV panel suppliers are planning to mass produce 8K displays in 2018. The 7680 x 4320 pixel resolution display is expected to make up about 1% of the 60″-and-larger display market this year and 9% in 2020.
 Ricky Park, director at IHS Markit, said:
Ricky Park, director at IHS Markit, said:
“As UHD has rapidly replaced full HD in the super large-sized TV display market, panel makers are willing to supply differentiated products with higher resolution and improve profit margin with premium products. Year 2018 will become the first year of the 8K resolution TV display”.
Innolux started developing 8K panels in 2017 and produced its first ever 8K LCD TV display (60Hz, 65″) in the fourth quarter of 2017. The display will be supplied to Sharp TV and Chinese brands to begin with. Meanwhile, Sharp also mass produced its first 8K LCD TV display at 70″ in the last quarter of 2017 to support the Sharp TV brand in China.
Looking at the 8K display roadmap in 2018, it appears that Samsung Electronics and Sony are driving the market at this time. They plan to release their flagship 8K TV models in 2018. Samsung and Sony will consume almost all 120Hz 8K panels from Innolux, AUO and Samsung Display, with sizes varying from 65-85″.
BOE and CEC-Panda are now planning to develop 8K LCD TV panels in the second half of 2018. Taking on a differentiation strategy, LG Display will likely focus on developing OLED 8K panels in the future. The company unveiled the world’s first 88″ 8K OLED TV display at CES 2018.
Based on current plans, panel makers in the early stages of development will mostly develop 60Hz 8K displays based on a-Si technology and those in the next stages are also likely to develop 120Hz 8K displays based on oxide technology. The latter has advantages, such as a better aperture ratio and lower power consumption.